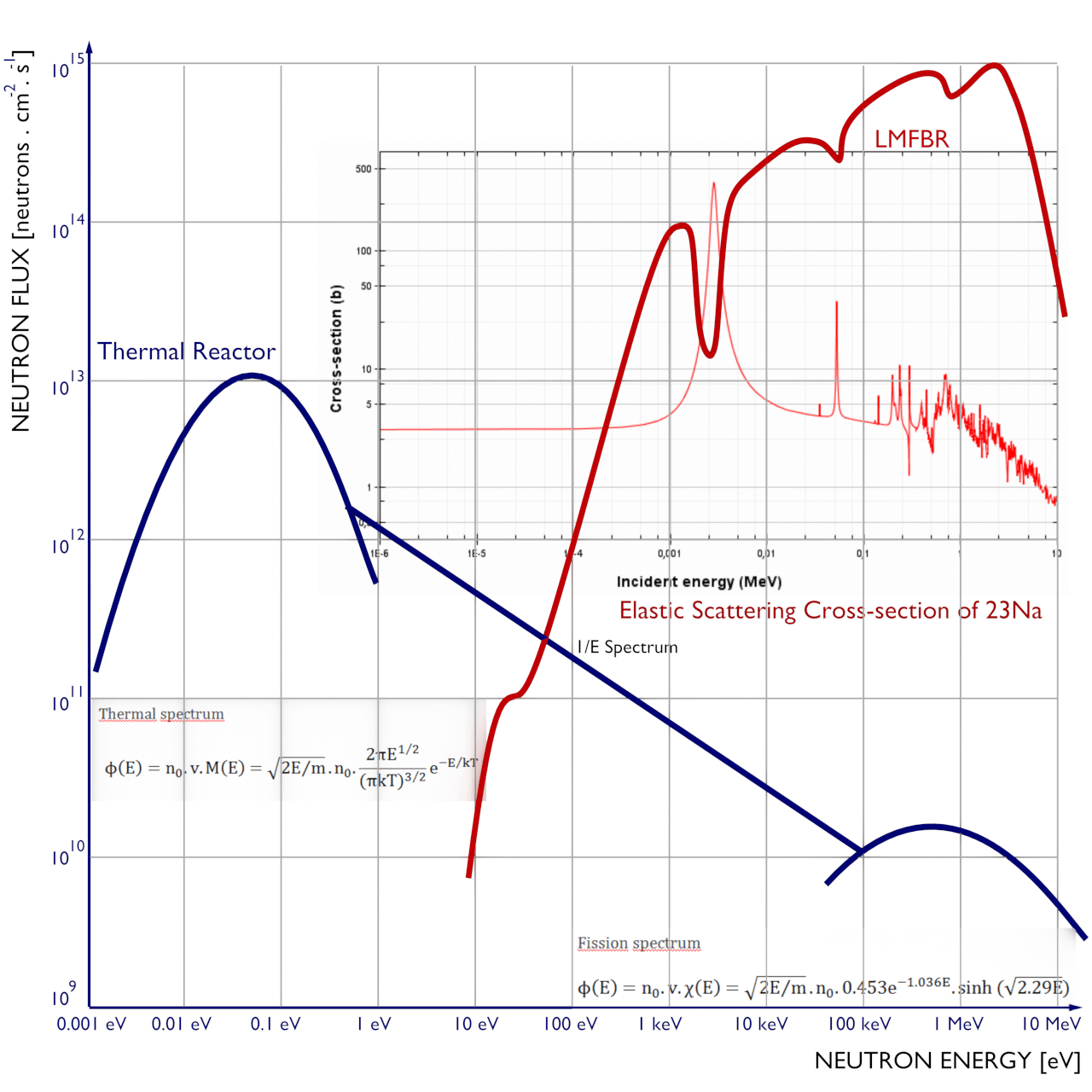
Neutron Flux differences in LMFBR vs Thermals
This image shows the major differences in Thermal and LMFBR enutron energy with the neutron flux as the y axis and energy as X. As neutron flux increases, thermal experiences a major slope downwards while in the .001 eV to 10 eV range, LMFBR doesn't even play a role - it is at a very high neutron flux and energy that LMFBR is effective
Back to Thermal ReactorThermal ReactorA thermal reactor describes a Nuclear Reactor with the main function of producing thermal heat to be converted to electricity. This term describes all of the operating reactors today with the exception of Fast Neutron Reactors. A thermal reactor is one in which neutrons are necessary to sustain a fissile reaction that creates heat: unlike a FNR that has an excess of neutrons. A thermal reactor specifically uses thermal neutrons - that are slower then fast neutrons. Thermal neutrons ahve the ben Back to Fast Neutron ReactorFast Neutron ReactorA Fast Neutron Reactor is a specific type of reactor that different from a Thermal Reactor-- it is not very common because unlike a thermal reactor that uses neutron to sustain the chain reaction, a FNR has no neutron moderation and less primary coolant due to an excess of fast neutrons * the capture to fission ratio is lower is fast reactors * high number of neutron produced per one fission * Neutron Flux has differences too The following image shows the neutron flux differences 400 Neutron F